Spectral Doppler: Pulmonary Valve
Obtaining the spectral Doppler
- Identify the pulmonary valve (PV) in the mid-esophageal views. The following two-dimensional TEE views can be used:
- Align the continuous wave (CW) cursor within the centre of the pulmonary artery (PA) or place the pulsed wave (PW) sample volume box at the level of the PV cusps (figure 1).
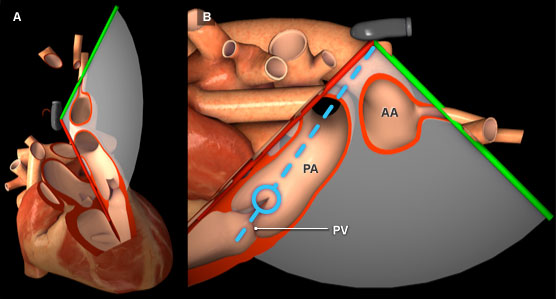
Figure 1: Three-dimensional heart model shown in cross-section to highlight the position of the TEE plane in the upper esophageal aortic arch short axis view. A) Anterior view of the heart with TEE plane. B) Right lateral view of the heart and TEE plane. The blue dotted line represents the orientation of the pulsed wave cursor and the blue circle indicates the position of the sample box at the tip of the pulmonary valve leaflets. Key: AA = Aortic Arch, PA = Pulmonary artery, PV = Pulmonary valve.
Features of pulmonary valve spectral Doppler
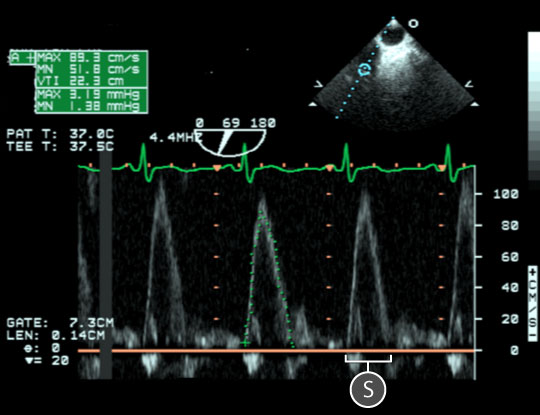
Figure 2: Plused wave spectral Doppler data acquired for blood flow through the pulmonary valve. In the upper right, a two dimensional TEE image of the upper-esophageal aortic arch short axis view; the blue circle indicates the location of the sample volume at the tip of the pulmonary valve leaflets. In the lower half of the image, a spectral doppler trace shows the relationship between blood velocity and time. Notice that the waveform is above the baseline as blood flows towards the transducer. The baseline is orange. Key: S = Systolic wave.
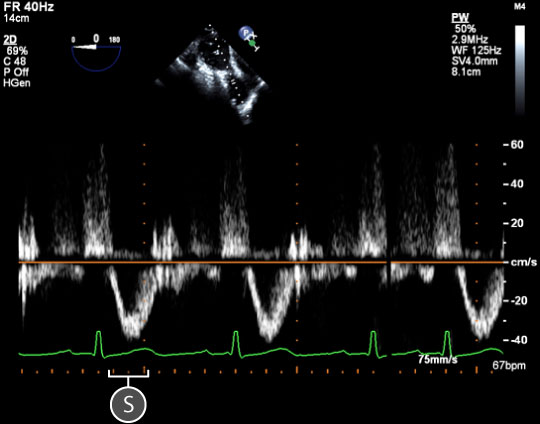
Figure 3: Pulsed wave spectral Doppler data acquired for blood flow through the pulmonary valve. In the upper left, a two dimensional TEE image of the modified transgastric basal view. In the lower half of the image, a spectral Doppler trace shows the relationship between blood velocity and time. The baseline is orange. Key: S = Systolic wave.
- The trace includes a single systolic waveform.
- Within the upper esophageal aortic arch short axis view, the waveform is above the baseline as blood flows toward the transducer (figure 2).
- Within the transgastric views, the waveform is below the baseline as blood flows away from the transducer (figure 3).
- Compared to the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) and aortic valve (AV) Doppler, the waveform has a slower rate of acceleration (upstroke) due to the lower distal vascular resistance.
- The PV wave Maximum velocity (VPV) is 80 – 100 cm/sec.
Physiological variation
- Pre/afterload dependence
Pathological variation
- Pulmonary valve disease
- Pulmonary artery hypertension
- Shunts
