Content
Module 2: Ancillary Equipment
Introduction
This module covers the additional equipment utilized in a bronchoscopic intubation. The bronchoscope (module 1) and equipment for applying local anaesthesia (module 4) are covered elsewhere.
Endotracheal Tube (ETT)
The choice of ETT depends on the intended site of intubation (oral vs. nasal), intended duration of intubation, availability and operator preference.
Size
The ETT should be large enough to fit over the chosen bronchoscope but small enough to pass through the nasopharynx (for nasal intubation). A smaller ETT is less likely to be difficult to advance over the bronchoscope as this avoids a size discrepancy between bronchoscope and ETT. Size 6 – 7mm is suitable for most adults. A smaller diameter ETT may be shorter, which should be taken into consideration for nasal intubation.
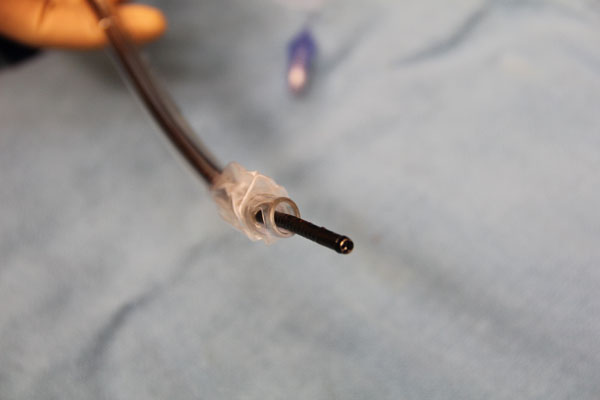
This is a size 8 ETT and bronchoscope with outside diameter 4.3mm.
ETT Choices
The table below outlines several choices of endotracheal tubes with their advantages and disadvantages.
Oral Intubation Devices
Several devices assist with oral bronchoscopic intubation, with the aims of:
- providing a passage for the scope
- protecting the scope should the patient bite down
- ensuring the scope is midline
- holding the tongue forward
Berman Airway
The Berman airway can be opened wide to disengage it from the ETT. Because it is quite long, if it is not in line with the glottis, passing the bronchoscope into the larynx can be challenging as the bronchoscope cannot be manoeuvred within the Berman airway. Withdrawing the airway partially can help.
Williams Airway
The Williams airway comes in two sizes: 90mm (accommodates an ETT size 8) and 100mm (accommodates ETT size 8.5). It requires removal of the 15mm connector from the ETT prior to removal of the airway. Similarly to the Berman, if it is not lined up with the glottis, manoeuvring the bronchoscope within the airway is difficult.
_sm.jpg)
Williams airway.
Ovassapian Airway
The Ovassapian airway comes in one size (accommodates ETT up to size 8.5). It can be 'opened' wide to disengage it from the ETT. It has a flat lingual portion to minimize movement from the midline and the open space assists with manoeuvring the bronchoscope.
_sm.jpg)
Ovassapian airway.
Aintree Catheter
When loaded on the bronchoscope, only the distal 3-4cm of the bronchoscope protrudes from the end, allowing manoeuvring. The pediatric size bronchoscope is placed in the lumen of the Aintree catheter. Both devices are then placed together – via a supraglottic airway or oral intubating device or via the nose. The bronchoscope is removed and the endotracheal tube is then railroaded over the Aintree catheter.
_sm.jpg)
Inner diameter: 4.8mm (bronchoscope must have outside diameter of 4.4mm or less). Outer diameter: 6.5mm (muse use ETT of 7.0mm or greater). Length: 56cm.
Video: ETT railroaded over Aintree catheter.
Continue to: Module 2: Advanced Knowledge

_thumb.jpg)
_thumb.jpg)
_thumb.jpg)
_thumb.jpg)


