Content
Module 1: The Bronchoscope
Introduction
This module covers the mechanics, specifics and care of the bronchoscope.
Components
Numbered descriptions of the parts of the bronchoscope below can be matched to numbers on images of the fiberoptic and video bronchoscope.
- Eye piece: Can be attached to a camera for display on screen. fiberoptic scopes have an eye piece; video scopes do not.
- Diopter ring for focusing
- Control lever: Controls the tip. Only permits movement in a vertical plane. Two wires extend from the handle to the tip in the insertion cord. Moving the lever down, moves the tip up and moving the lever up, points the tip down. Side to side movement is accomplished by rotation of the body of the bronchoscope with the operator's wrist and shoulder.
- Working channel port: For suction, instillation of local anesthetic, oxygen delivery.
- Body: Incorporates the eye piece, diopter ring, control level and working channel. Grasped by the operators non-dominant hand.
- Insertion cord: Contains fiberoptic bundle for light and image transmission, tip bending control wires and working channel. Average length 600mm (range 500 – 650mm).
- Light source: Can be a portable battery powered source or via a cable. Light source may be halogen, incandescent or LED.
- Suction valve and port
Fiberoptic Bronchoscope
_sm.jpg)
_sm.jpg)
Video Bronchoscope
_sm.jpg)
_sm.jpg)
Examples
Several examples of commonly used fiberoptic and videobronchoscopes are in the table below. For further information and for additional bronchoscopes, refer to the manufacturers websites:
- Olympus videobronchoscopes
- Olympus fiberoptic bronchoscopes
- Pentax fiberoptic and videobronchoscopes
Click on a table heading to scroll to an explanation below.
| SCOPE | TYPE | OD (mm) | Working channel (mm) | Length (mm) | Tip movement | Field of view (°) |
| PENTAX EB1570K | Video | 5.5 | 2.0 | 600 | Up 210° Down 130° |
120 |
| PENTAX FB-15V | Fiberoptic | 4.9 | 2.2 | 600 | Up 180° Down 130° |
120 |
| OLYMPUS BF P160 | Video | 4.9 | 2.0 | 600 | Up 180° Down 130° |
120 |
| OLYMPUS LF-V | Video | 4.1 | 1.2 | 600 | 120 | |
| STORZ 11301-BN | Fiberoptic | 5.2 | 2.3 | 650 | Up 140° Down 140° |
110 |
| STORZ 11302 BD | Fiberoptic | 3.7 | 1.5 | 650 | Up 140° Down 140° |
90 |
- Type: Is the bronchoscope a fiberoptic bronchoscope or videobronchoscope?
-
Outside diameter
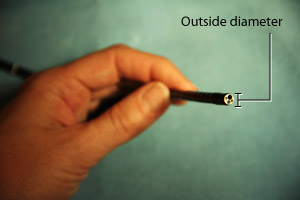
Outside diameter: Outside diameter of the insertion cord, in millimeters.
-
Working channel
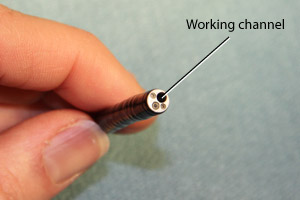
Working channel: Diameter of the working channel for suction, instillation of local anesthesia, etc.
-
Length
_sm.jpg)
Length: Length of the insertion cord.
-
Tip movement

Tip movement: Degrees of movement of the tip of the bronchoscope up.

Tip movement: Degrees of movement of the tip of the bronchoscope down.
- Field of view
_sm.jpg)
Field of view: The area that can be observed without angulation.
Care of the bronchoscope
- Avoid bending any part of the insertion cord other than the tip, which may result in breakage of the fiberoptic fibers.
- Avoid twisting the insertion cord which can also break fiberoptic fibers. Rotation should be from the body of the bronchoscope.
- Use a bite block in awake / unparalyzed patients to prevent inadvertent biting of the scope.
- Store with the insertion cord straight.
Checklist prior to use
- Bronchoscope sterilized
- Check tip movement
- Suction valve attached and suction available
- Light source attached and operational
- Connect bronchoscope to monitor if using a screen and ensure correct orientation
- Defog tip of scope and white balance
- Focus the eyepiece or monitor on some written words. Confirm integrity of image, i.e. no pixel drop-out
- Lubricate the scope and load the ETT, securing it into place with a piece of tape
Continue to: Module 1: Advanced Knowledge

