Indications
Laparoscopy for gynecologic surgery is used to diagnose or treat conditions of the abdomen and pelvis.

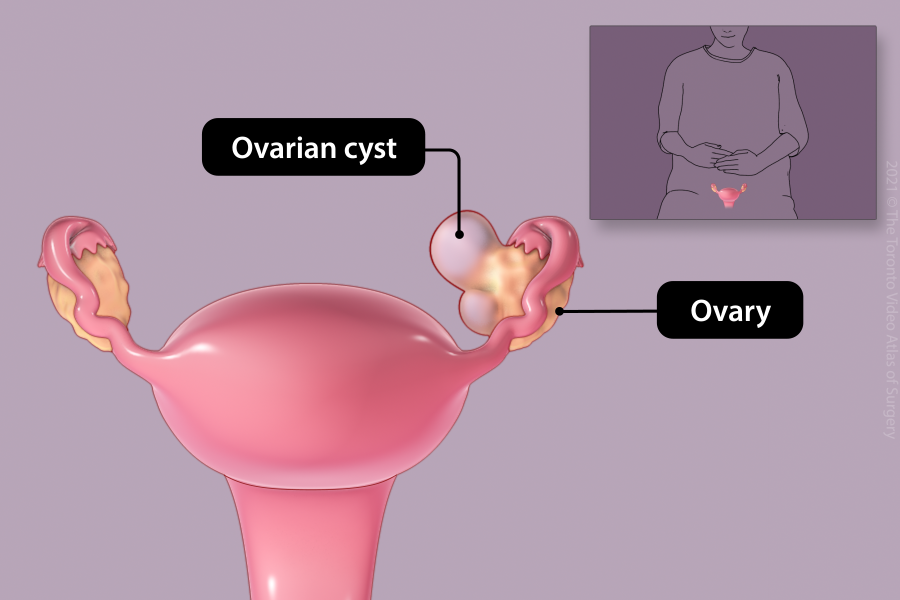
Removal of ovarian cyst (Cystectomy)
Ovarian cysts are growths on the ovaries. These cysts are removed if they cause symptoms (pain or pressure), are large, or look abnormal.
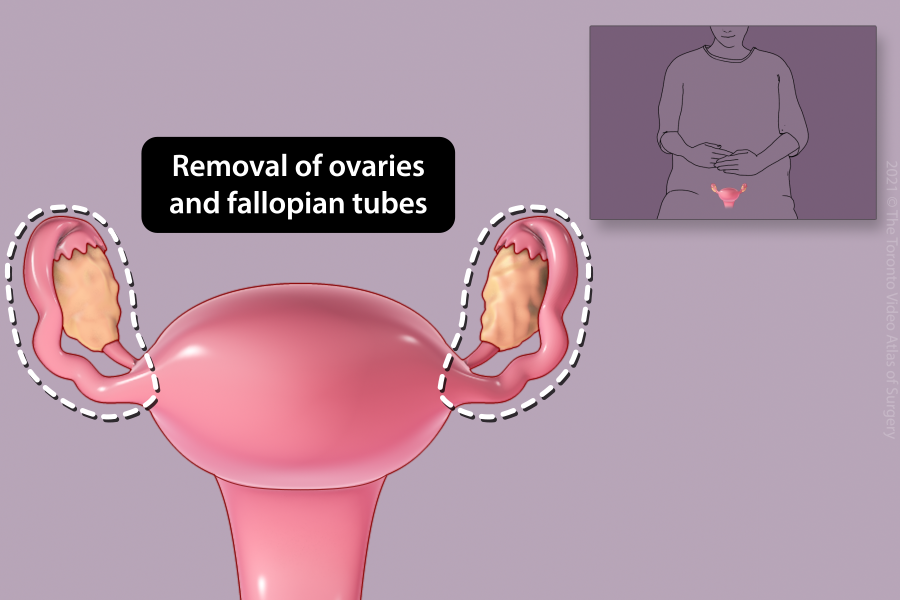
Removal of ovary (Oophorectomy)
Depending on your age or other medical conditions, your doctor may recommend removal of one or both ovaries. In general, the fallopian tube on the same side is removed with the ovary (salpingo-oophorectomy).
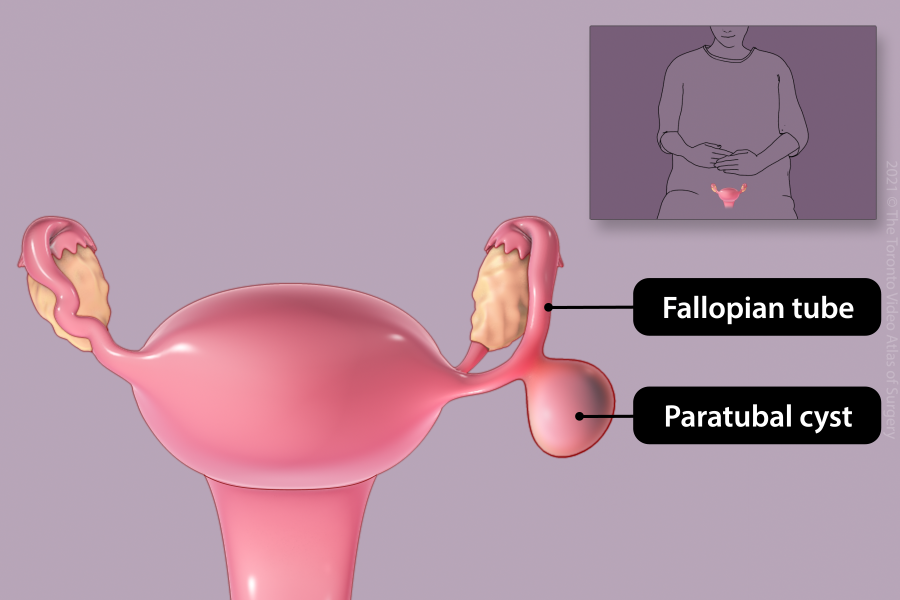
Removal of fallopian tube cyst (Paratubal cystectomy)
Paratubal cysts are growths on the fallopian tubes. These cysts are removed if they cause symptoms (pain or pressure), are large, or look abnormal.
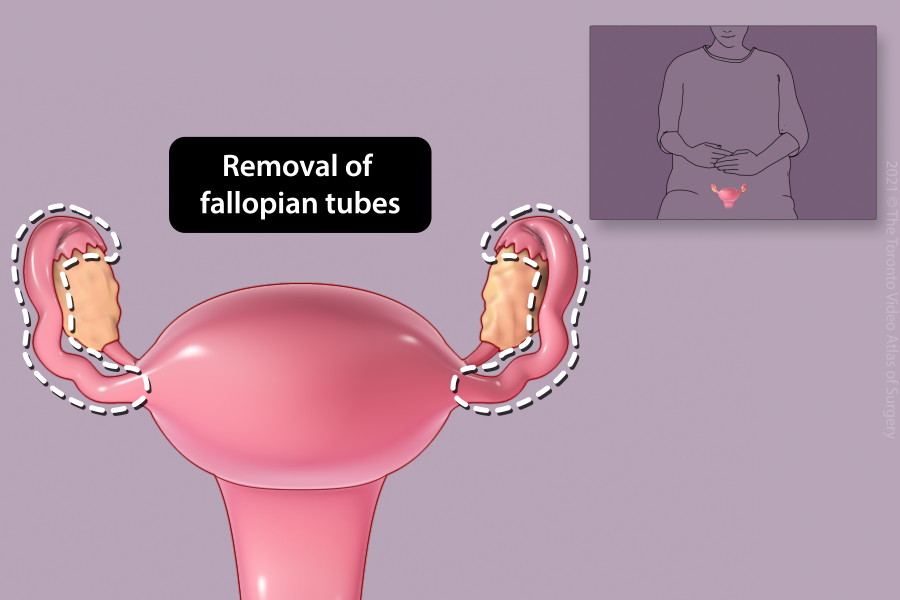
Removal of fallopian tube (Salpingectomy)
The most common reason for the removal of a single fallopian tube is to surgically treat an ectopic pregnancy. Other reasons to remove one or both fallopian tubes include damaged tubes, pregnancy prevention, or ovarian cancer prevention.
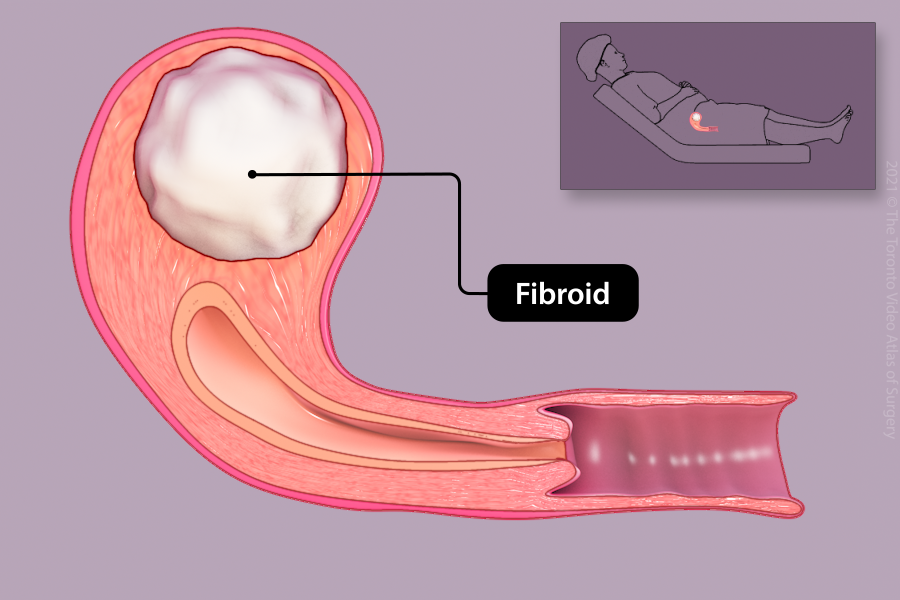
Removal of fibroid (Myomectomy)
Fibroids are benign growths within the uterus. Fibroids may be removed if they are large, symptomatic (pressure or heavy bleeding), or cause difficulty getting pregnant. Depending on the number, size, and location, they can be removed laparoscopically.
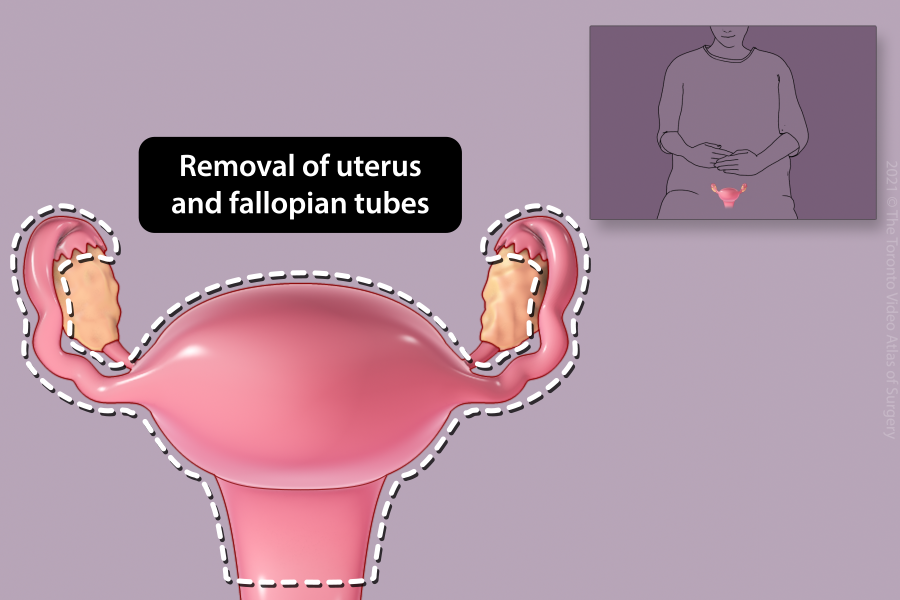
Removal of the uterus (Hysterectomy)
The uterus may be removed for pain or heavy bleeding not controlled by medications, large fibroids, prolapse or cancer. Generally, both fallopian tubes are removed at the time of hysterectomy to decrease the risk of developing ovarian cancer in the future. The ovaries may be removed at the time of hysterectomy depending on your age, menopausal status, or indication for the surgery.
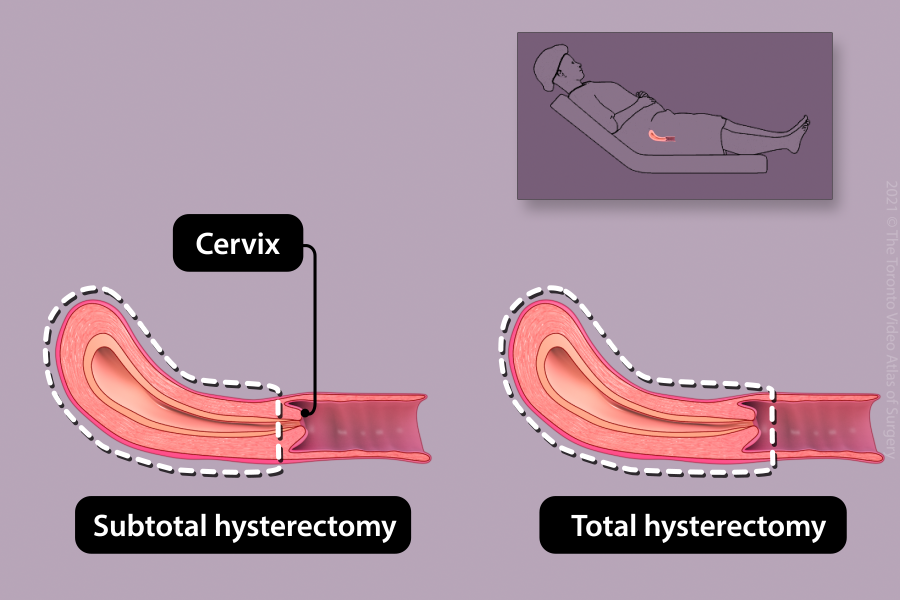
Types of hysterectomies
There are different types of hysterectomies:
- Total: The uterus and cervix are removed (most common)
- Subtotal: The uterus is removed, but the cervix is left in place
Depending on the size of the uterus, it may be removed laparoscopically.
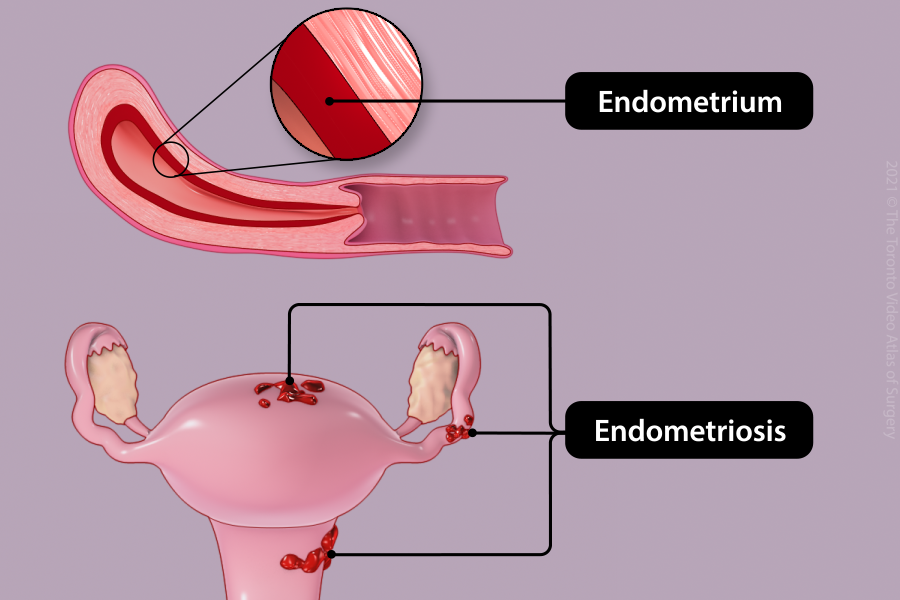
Management of endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when cells of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) are found outside the uterus. This can cause painful menses, chronic pelvic pain, difficulty getting pregnant, and/or ovarian cysts. During laparoscopy, endometriosis tissue may be destroyed or removed, and scar tissue broken down to re-establish normal anatomy.
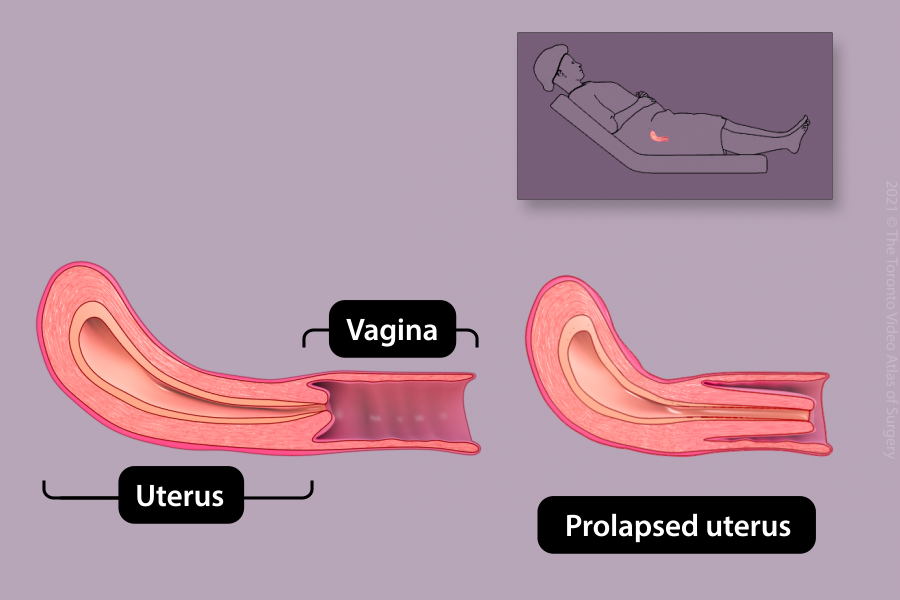
Repair of prolapse and incontinence
Some procedures to fix prolapse (uterus or vagina falling down) or incontinence (difficulty with bladder control) can be performed laparoscopically.