Procedures

Your obstetrical care provider will review your medical history and perform a vaginal examination to determine the most appropriate method for induction. Your induction of labour can involve one or a combination of the following methods.
Induction of labour: Overview
Induction of labour involves using various methods to start (induce) labour. This process can be divided into two phases:
- Phase 1: Soften, thin, and dilate the cervix (cervical ripening)
- Phase 2: Start uterine contractions
If the cervix is already soft/thin/dilated (favourable or ripe), your induction of labour may start directly at phase 2.
These methods are used to soften, thin, and dilate a cervix that has not yet started to change for labour.
You may be discharged home or admitted to hospital for this portion of your induction, depending on the clinical scenario.
Mechanical
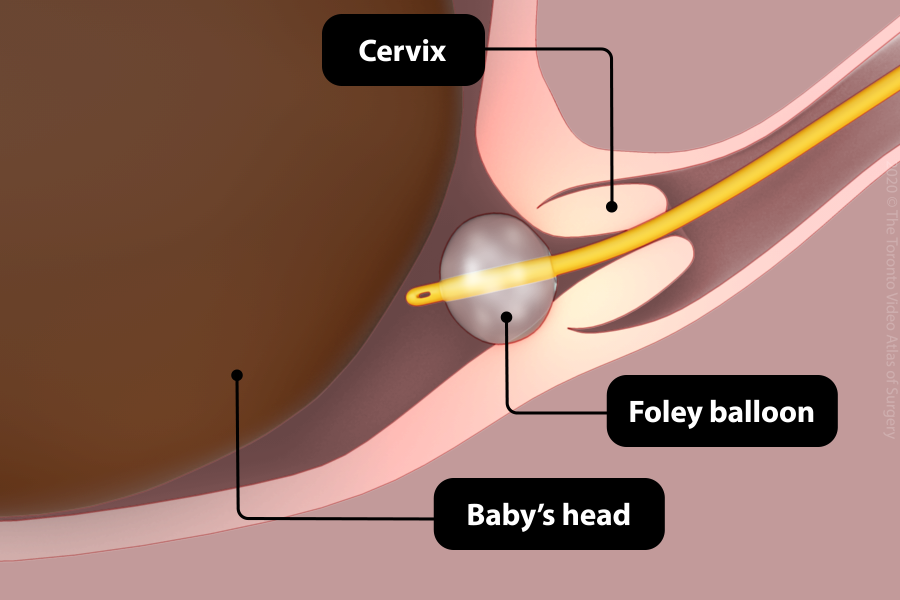
Foley catheter
- A thin tube (Foley catheter) with a small balloon at the tip is inserted past the cervix, usually with a speculum placed in the vagina to visualize the cervix.
- The balloon is then inflated so that it sits between the baby’s head and the cervix.
- The tube is taped under tension to your leg. The balloon places mechanical pressure on the cervix, causing the cervix to soften and open. Once the cervix is 3-4 cm dilated, the balloon falls out.
Hormonal
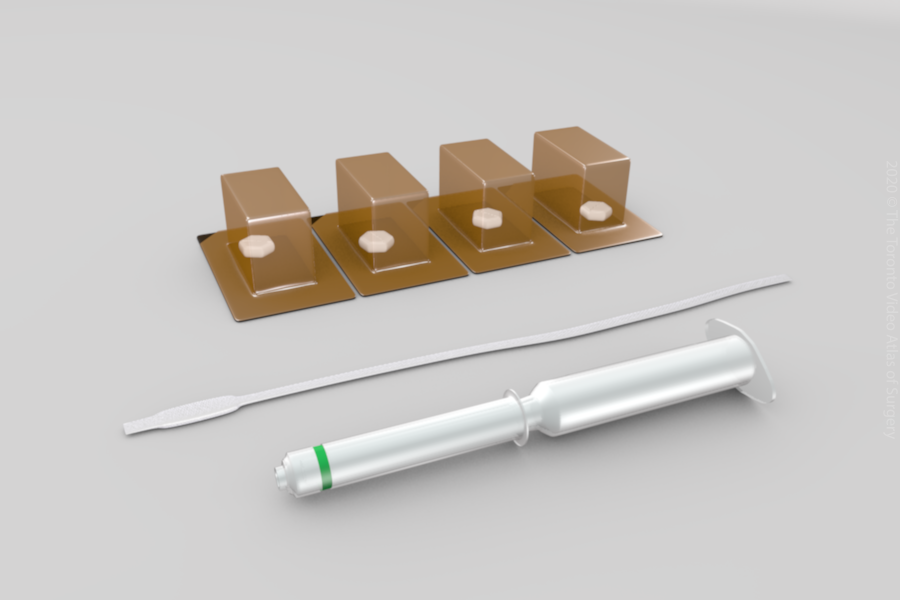
Prostaglandins
- Prostaglandins are hormones produced by the body that soften, thin, and dilate the cervix as well as cause uterine contractions. They are not recommended for patients who have had a previous Cesarean section.
- Prostaglandins are available in several forms.
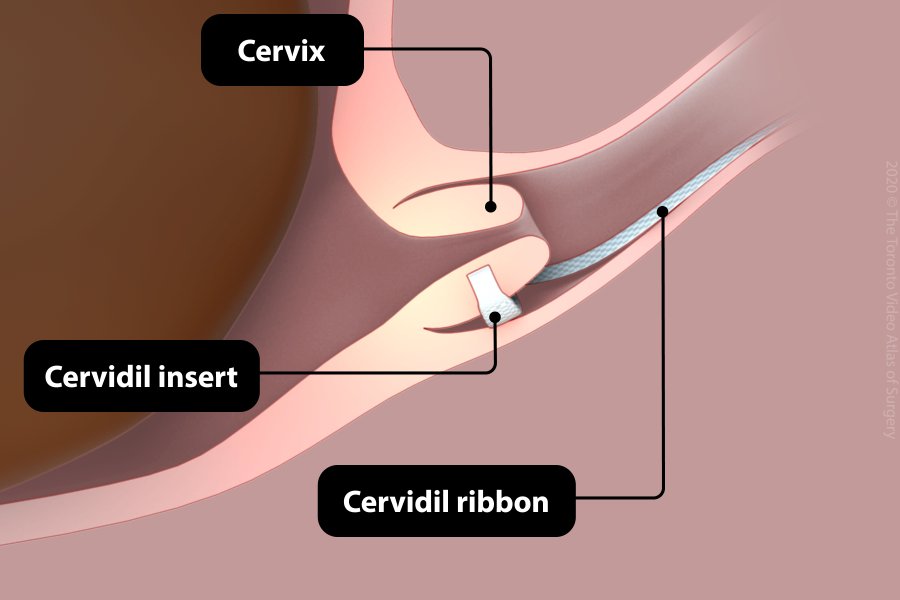
Prostaglandins - Cervidil
- This is a prostaglandin vaginal insert that is attached to a ribbon.
- The insert is placed behind the cervix and the ribbon end is left outside the vagina so that it can be easily removed.
- Cervidil releases prostaglandins over 12-24 hours, at which point it is removed.
- If the first Cervidil has not ripened the cervix enough, a new Cervidil or another method of cervical ripening can be used.
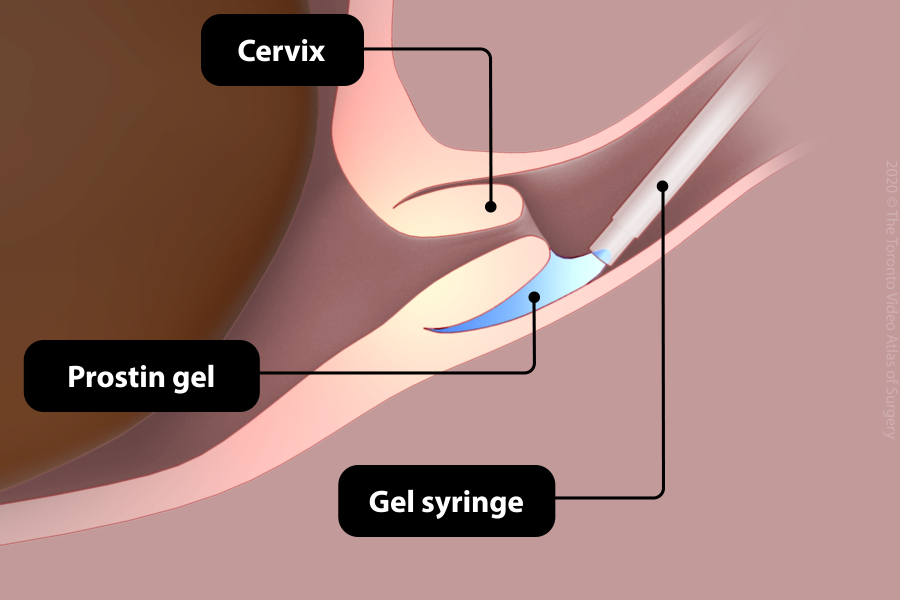
Prostaglandins - Prostin gel
- This is a gel containing prostaglandin that is inserted into the vagina behind the cervix.
- After 6 hours, the gel (or another method of cervical ripening) can be administered again if the first dose has not produced the desired result.
- Unlike Cervidil, the gel cannot be removed.
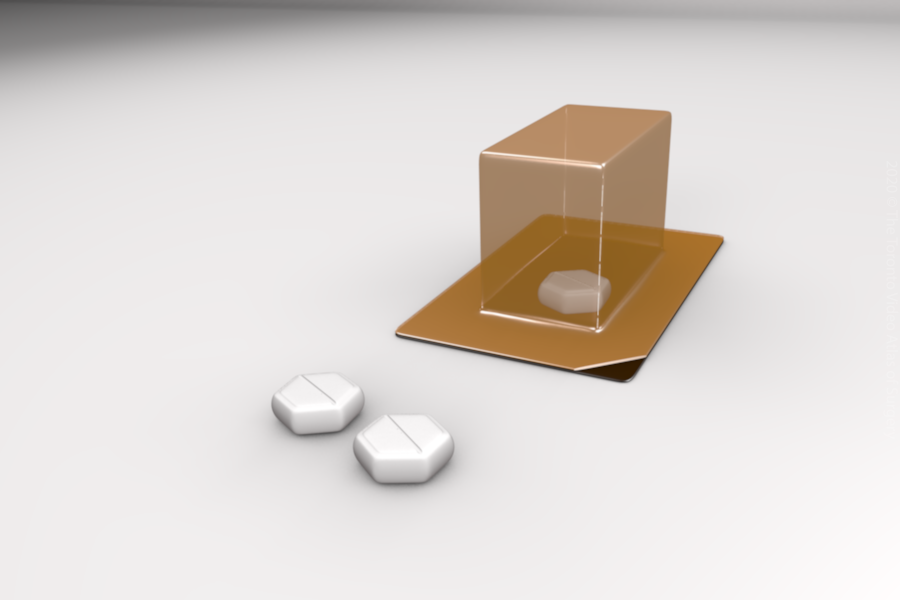

Prostaglandins - Misoprostol
- This is a prostaglandin tablet that may be either inserted into the vagina or taken by mouth.
- Misoprostol can be used both for cervical ripening as well as to produce contractions (Phase 2).
- The tablet can be administered every 2-4 hours until the desired result is achieved.
These interventions are used once the cervix has started to change for labour (i.e. the cervix is soft, thin,
and at least 2 cm dilated). You will be admitted to hospital for this phase of the induction process.
Mechanical
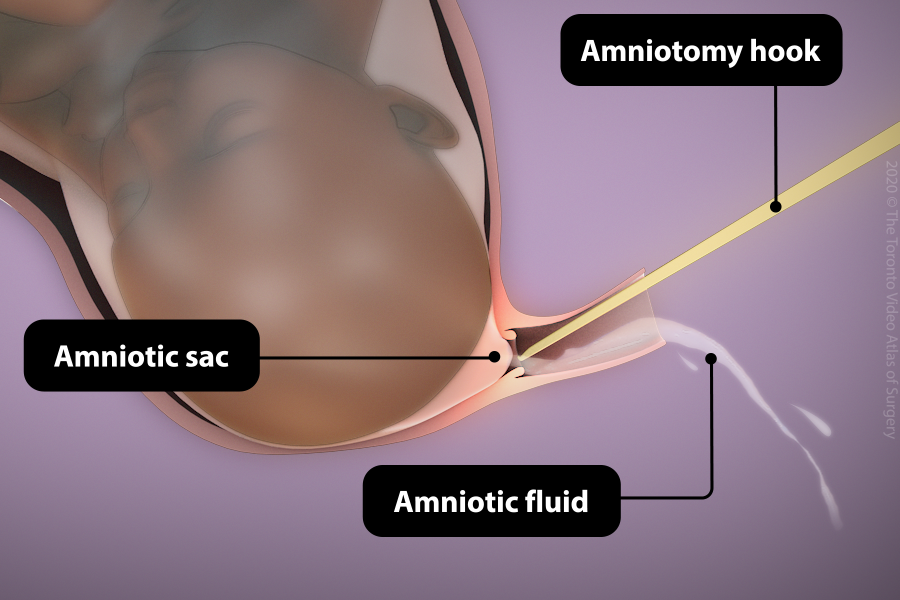
Artificial rupture of membranes (Amniotomy)
- Once the cervix is favourable (usually at least 2cm dilated) and the baby’s head is against the cervix, the membranes are ruptured (“breaking the water”).
- Amniotic fluid contains prostaglandins, which cause cervical ripening as well as contractions.
- A plastic hook is inserted into the vagina to gently open the amniotic sac. This procedure does not harm you or your baby.
- After the amniotic sac breaks, you will feel ongoing leaking of amniotic fluid from the vagina until delivery.
Hormonal

Oxytocin
- Oxytocin is a hormone produced by the body that causes uterine contractions.
- It is given through an intravenous (IV) line to start or increase contractions.
- A small amount is started and increased slowly until the contractions are strong and close together.
- When you are on oxytocin, your contractions and the baby’s heart rate are continuously monitored.

Prostaglandins - Misoprostol
- Also used in Phase 1 to ripen the cervix, misoprostol is a prostaglandin tablet that may be either inserted into the vagina or taken by mouth.
- The tablet can be administered every 2-4 hours until the contractions are strong and close together.
- When you are being induced with misoprostol and are in labour, your contractions and the baby’s heart rate will be continuously monitored.