ROBOTIC HYSTERECTOMY
For patients with high BMI
00:09 Introduction
01:35 Benefits of robotic surgery in high BMI patients
02:53 Patient positioning
03:59 Uterine manipulator insertion
04:35 Port placement
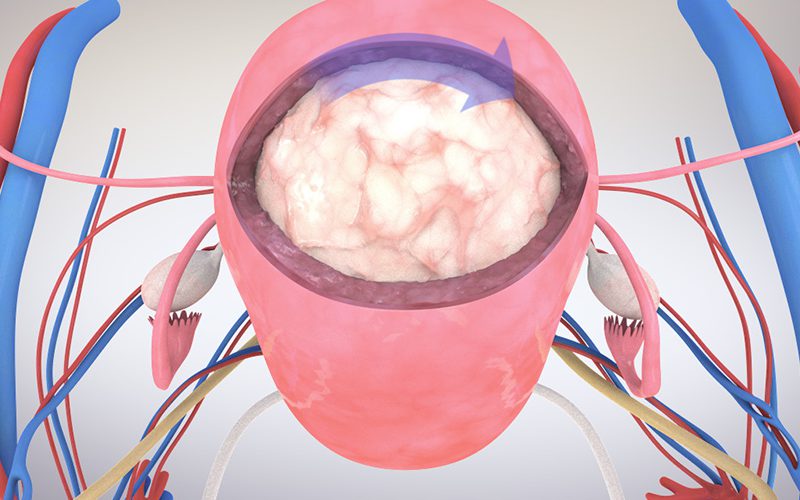
06:08 Operation
Case description
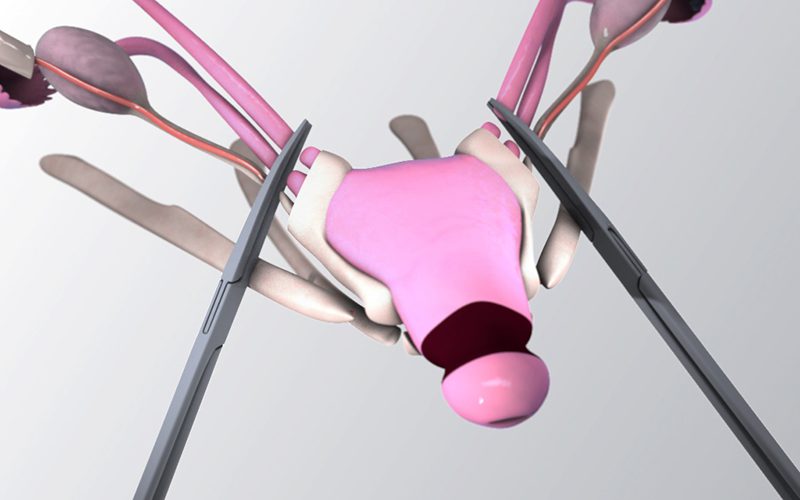
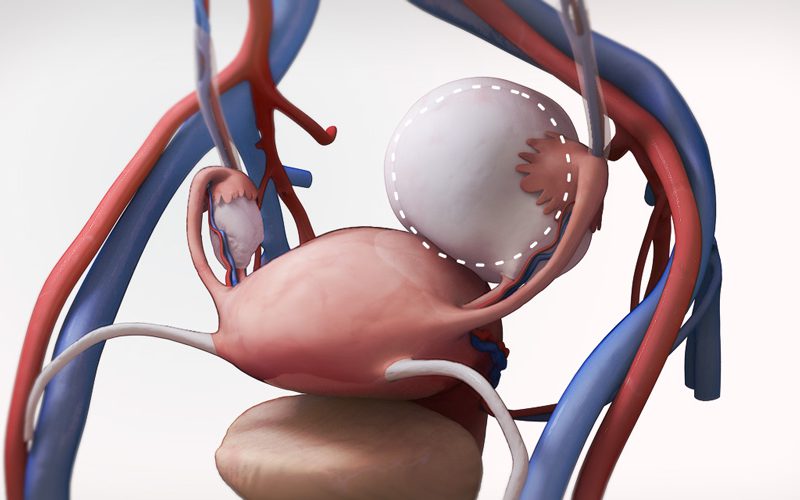
- Robotic assisted total laparoscopic hysterectomy, and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy,
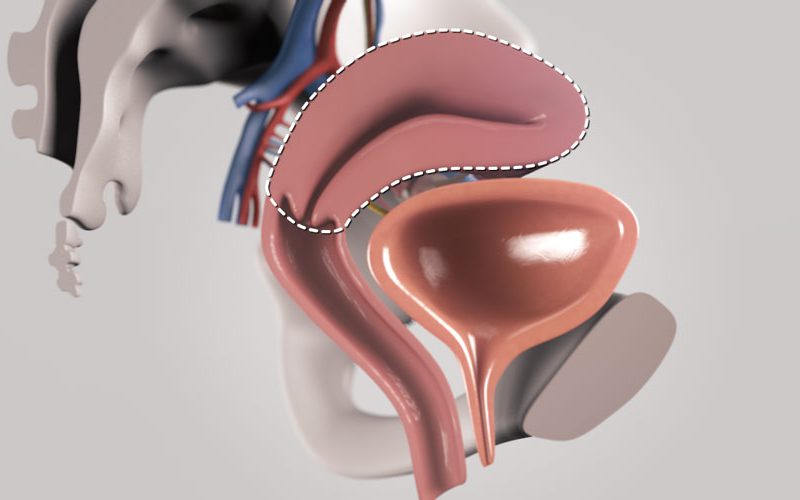
is most commonly performed in patients with endometrial pathology,
and an elevated body mass index (BMI > 40) - There are several benefits of using robotic assistance when performing laparoscopic
hysterectomy in patients with elevated BMI, including 'arm bumping', where the robot acts to lift the patient’s abdominal wall, allowing the surgery to be performed at a lower intra-abdominal pressure, and facilitates improved ventilation in steep Trendelenburg. - The robot also allows for improved ergonomics for the surgical team members, and improves surgical feasibility in patients with elevated BMI.
- The robot employs a third arm, which allows for the use of additional instruments
that can aid in visualization and retraction through the surgery. - The robot also allows for increased surgical dexterity, as robotic instruments can rotate a full 360 degrees, and act like a human hand or wrist, making it easier to work in small spaces and at difficult angles.
- During patient positioning, padding is placed around the shoulders, forearms, and wrist, to avoid excess pressure throughout the case, and decrease the risk of intra-op nerve injury.
- If there is a large pannus, sandbags are clipped to the patients pannus, and pulled towards the patient’s feet once in Trendelenberg, taking pressure off the lungs to facilitate ventilation by anesthesia, and to displace the pannus and return the umbilicus to a more natural position.
- Placement of the uterine manipulator can be challenging in patients with elevated BMI, and may require two assistants. The patient's legs should be brought upwards and outwards for the optimal set up.
- Port placement configuration can differ depending on the robot used. This video showcases the 'rainbow' pattern port placement.
- Once the ports are placed, prior to docking the robot, the surgical team should confirm with anesthesia that the patient is tolerating steep Trendelenburg, as the bed cannot move after the robot is docked.