Techniques for Induction of Labour
00:17 Introduction
01:41 Cervical ripening: Mechanical
05:21 Cervical ripening: Hormonal
11:31 Amniotomy
13:16 Oxytocin administration
OTHER LANGUAGES
- Induction of labour involves the artificial process of cervical ripening and uterine contractions with the goal of a vaginal delivery. This video provides an overview of techniques used in mechanical cervical ripening, hormonal cervical ripening, amniotomy and oxytocin administration.
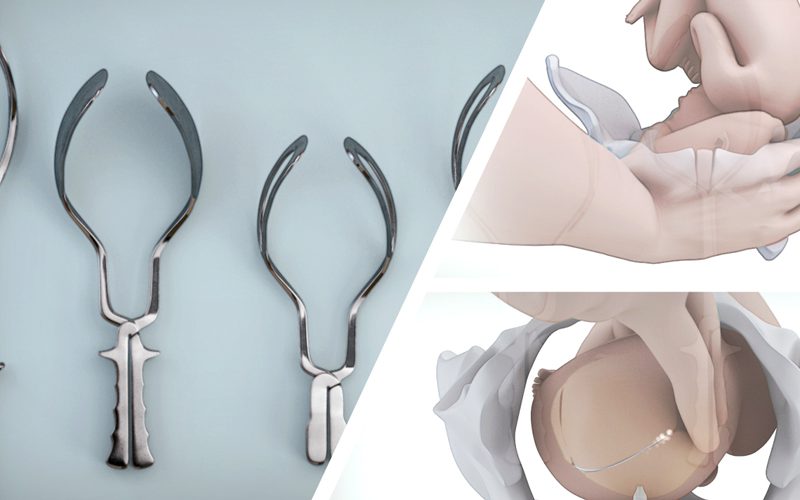
- Mechanical cervical ripening utilizes a Foley balloon catheter, exerting pressure on the cervical canal and lifting fetal membranes, which triggers the release of endogenous prostaglandins.
- Hormonal ripening involves administration of PGE1 orally or vaginally, or applying PGE2 to the posterior cervical fornix.
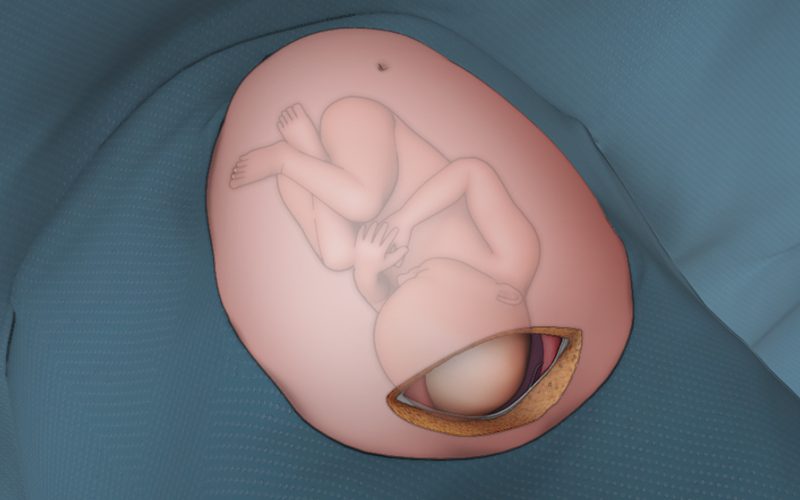
- Aminotomy is performed once the cervix is favourable, and involves puncturing the membrane with an amniotic hook, eleasing the prostaglandins within the amniotic fluid.
- The final step in the induction of labour pathway is oxytocin administration to stimulate and optimize uterine contractions.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cervical Dilation (cm) | 0 | 1-2 | 3-4 |
| Effacement (%) | 0-30 | 40-50 | 60-70 |
| Station (ischial spines) | >=-3 | -2 | -1/0 |
| Cervical consistency | Firm | Medium | Soft |
| Cervical position | Posterior | Mid | Anterior |
| Indications | Contraindications | Cautions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foley | Unfavorable cervix
Previous Cesarean Section |
Ruptured Membranes
Undiagnosed Vaginal Bleeding Simultaneous use of prostaglandins Low lying placenta Abnormal FHR |
Polyhydramnios |
| Prostagladin E2 (dinoprostone) | Unfavorable cervix | Known Hypersensitivity
Previous CS or uterine surgery Undiagnosed Vaginal Bleeding Muliparity >6 term pregnancies Overdistension of the uterus (multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios) |
Suspicion of cephalopelvic
disproportion Asthma, COPD (may cause bronchospasm) Epilepsy with poorly controlled seizures Glaucoma Ruptured membranes (Cervidil) you can use prostin gel with ROM Avoid concurrent oxytocin use |
| Prostaglandin E1 (misoprostol) | Unfavorable cervix | Known Hypersensitivity
Previous CS or uterine surgery Undiagnosed Vaginal Bleeding |
|
| Artificial Rupture of membranes | After cervical ripening
Favorable cervix |
Poor application of the presenting
part/unstable lie Fetal head not engaged |
|
| Oxytocin | IOL with ruptured membranes | Less than 30 minutes following removal
of prostin pessary Less than 6 hours following insertion of prostin gel Previous CS |