Assisted Vaginal Birth
Pelvic assessment and Obstetrical forceps selection
00:11 Introduction
00:39 Prerequisites for assisted vaginal birth
02:08 Abdominal exam
04:00 Vaginal exam: assessment of fetal position
06:27 Vaginal exam: assessment of fetal station
CASE DESCRIPTION
- Assisted vaginal birth (AVB) attempts to mimic spontaneous vaginal birth.
- Delivery by AVB may benefit both mothers and neonates by decreasing risks of serious morbidity associated with prolonged delays in delivery, or a caesarean delivery late in second stage.
- Various types of forceps or vacuum devices can be used to safely and successfully achieve vaginal delivery, provided the prerequisites for AVB are met.
- This video will discuss preliminary considerations to achieve safe forceps-assisted vaginal birth.
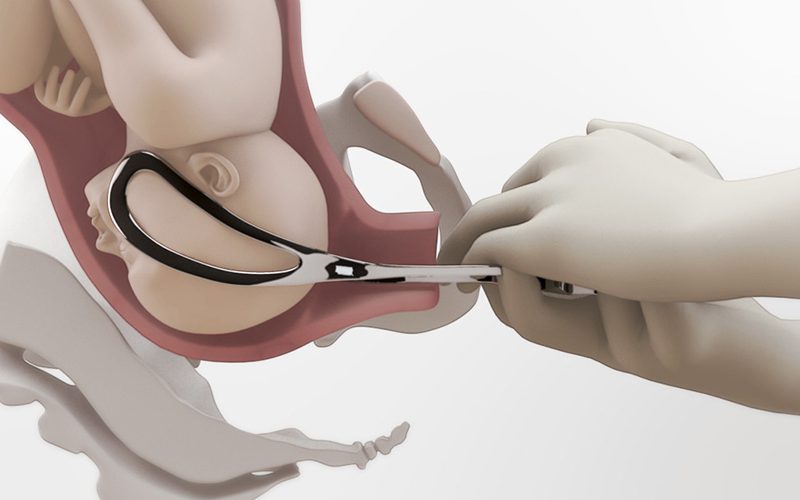
- A list of prerequisites known as FORCEPS must be met before assisted vaginal birth is attempted.
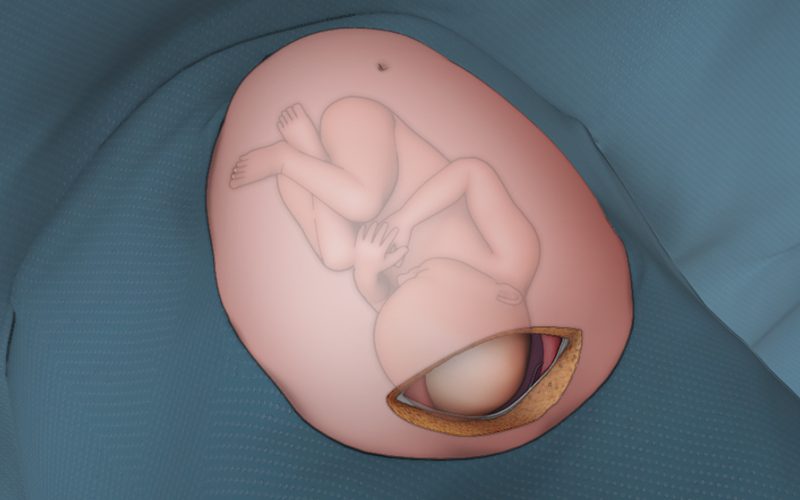
- F: Fully dilated
- O: Occiput anterior / posterior/ transverse
- R: Ruptured memberanes
- C: Cephalic presentation or head first
- E: Engaged presenting part, fetal head has descended to below the ischial spines
- P: Position patient, pain relief
- S: Sphincter bladder empty
- Comprehensive abdominal and vaginal examinations must be performed to confirm that the patient meets all criteria to proceed safely.
- Fetal head engagement is measured in fifth. The fetal head must be palpated at no more than 1 finger breadth or 1/5th above the pubic brim and at least at or below spines on vaginal exam in order to safely proceed with forceps delivery.